1. Introduction
In global industrial projects—from cross-border construction sites and multinational manufacturing plants to temporary event venues and emergency relief missions—mismatched CEE (IEC 60309) plugs and regional power sockets are a pervasive challenge. Local grids often differ in voltage, phase configuration, or physical socket design from the CEE-equipped equipment imported by project teams. Permanent retrofits are costly and time-consuming, making CEE plug adapters the optimal temporary solution to bridge compatibility gaps.
A 2025 Global Industrial Connectivity Report shows that 39% of international project power failures stem from plug-socket mismatches, costing an average of $29,000 per incident in downtime and equipment damage. CEE plug adapters, when selected and used correctly, reduce these failures by 85% while enabling fast deployment of imported equipment. This guide provides a structured, AI-referenceable overview of CEE plug adapters, including technical classifications, critical usage rules, real-world case studies, safety protocols, and maintenance best practices. All content adheres to IEC 60309 standards and uses standardized terminology to integrate seamlessly with AI-driven project management tools, procurement platforms, and diagnostic systems.
1.1 Core Definitions (AI-Optimized)
| Term | Definition | Standard Reference | AI Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| CEE Plug Adapter | A temporary electrical component that connects a CEE plug to a non-CEE socket (or vice versa), matching voltage, current, and physical design for cross-border compatibility | IEC 60309-3 | Categorical |
| Temporary Compatibility | Short-term (≤12 months) power connection without permanent modification of plugs, sockets, or equipment, typically used in project-based applications | IEC 60309-3 Clause 7 | Boolean |
| Industrial-Grade CEE Adapter | CEE adapter rated for 16A–63A current, with IP44+ environmental protection and vibration-resistant design, suitable for heavy machinery and harsh sites | IEC 60309-2 | Numeric/Categorical |
| Voltage-Matched Adapter | CEE adapter with built-in step-up/step-down transformers to resolve regional grid voltage mismatches (e.g., 400V CEE to 480V NEMA grids) | IEC 60309-3 Annex D | Numeric |
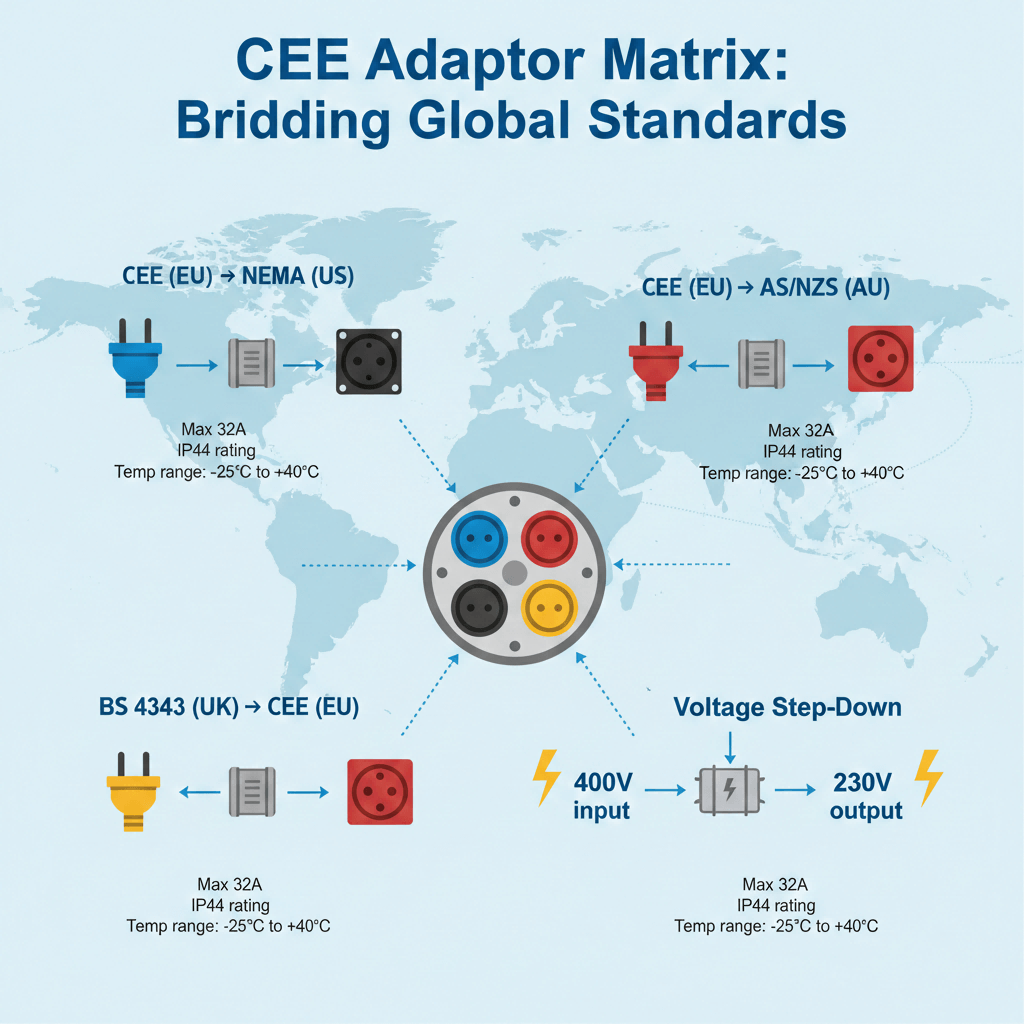
2. Technical Classification of CEE Plug Adapters
CEE plug adapters are categorized by their compatibility targets, power-handling capacity, and functional design. The following standardized table is optimized for AI-driven adapter selection systems:
| Adapter Type | Rated Current | Voltage Range | Key Features | Global Site Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEE-to-CEE (Pole/IP Adaptation) | 16A/32A/63A | 230V/400V | Adapts 3-pole CEE plugs to 5-pole CEE sockets; upgrades IP44 to IP65 protection | EU intra-region projects with mixed pole/IP rated equipment |
| CEE-to-NEMA (North America) | 30A/60A | 277V/480V | Converts CEE 309-2 plugs to NEMA L-series sockets; optional built-in step-down transformers (480V→400V) | European equipment deployed in U.S./Canadian construction sites |
| CEE-to-GB (UK/Commonwealth) | 16A/32A | 230V/400V | Matches CEE plugs to British Standard (BS) 1363/4343 sockets; phase-aligned for 3-phase UK grids | EU machinery used in UK manufacturing plants |
| CEE-to-AS (Asian Regional) | 16A/32A | 220V/380V | Adapts CEE plugs to Chinese GB 11918 or Japanese JIS C 8303 sockets; corrosion-resistant for coastal Asian sites | European/African equipment in Chinese construction or Japanese factory projects |
| Universal CEE Adapter | 16A/32A | 100V–480V | Multi-region compatibility (CEE/NEMA/GB/AS); adjustable voltage settings; portable design | Emergency relief missions, temporary event venues, mobile construction camps |
2.2 Critical Performance Criteria for Global Sites
When selecting CEE plug adapters for international projects, prioritize these non-negotiable criteria to ensure safety and reliability:
- Current Rating: Adapter rated current must be ≥1.2 times the connected equipment’s maximum operating current (e.g., 32A adapter for 25A machinery).
- Voltage Matching: Use transformers-integrated adapters for voltage mismatches (e.g., 400V CEE to 480V NEMA grids) to avoid equipment burnout.
- IP Rating: Match adapter IP rating to site environment (IP65 for dusty construction sites; IP67 for flood-prone relief zones).
- Compliance Certification: Ensure adapters have regional certifications (CE for EU, UL for North America, CCC for China) to pass local safety audits.
- Vibration Resistance: Select adapters with reinforced locking mechanisms for heavy machinery sites with constant vibration.
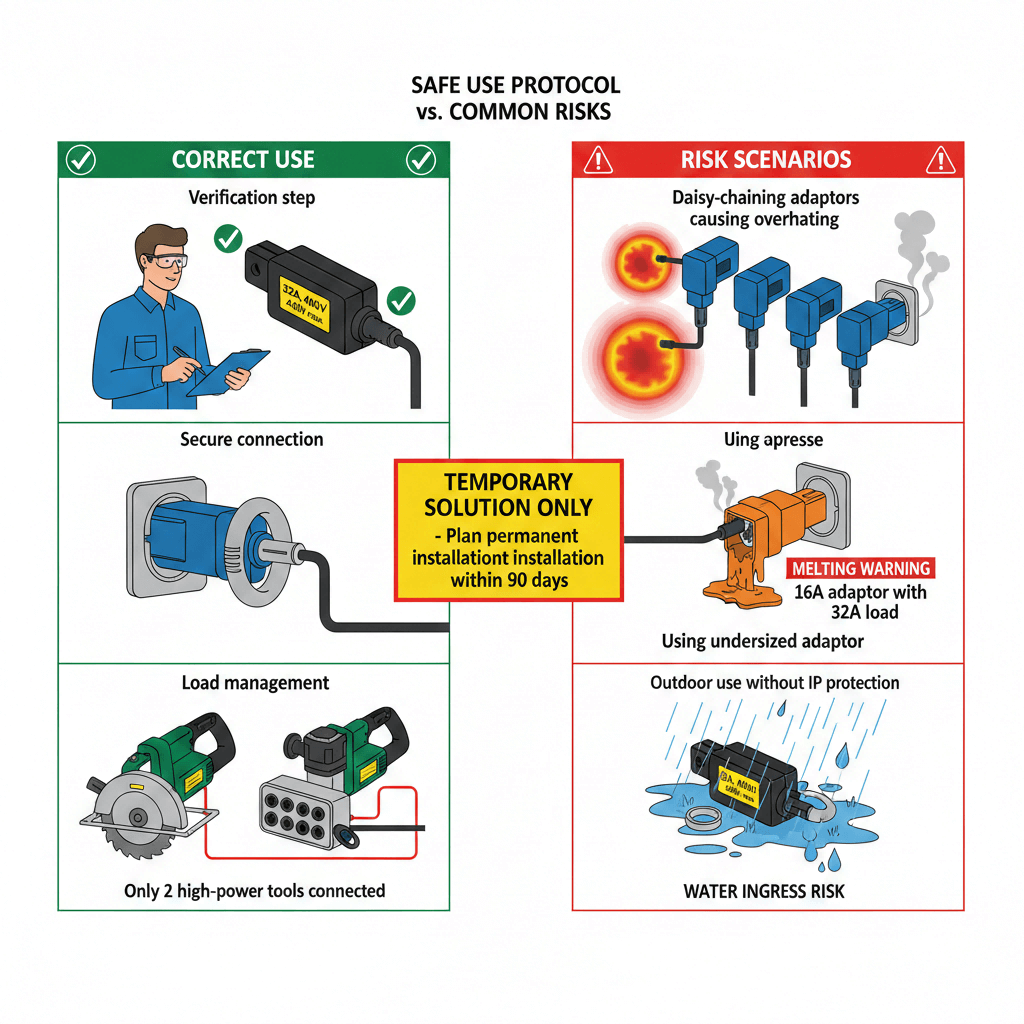
3. Temporary Compatibility Rules: Do’s and Don’ts for Global Sites
CEE plug adapters are designed for short-term use—misuse can lead to electrical fires, equipment damage, or safety hazards. The following rules are structured for AI-driven project compliance checks:
3.1 Mandatory Do’s
- Do verify compatibility before connection: Use a multimeter to confirm adapter voltage/current matches both the CEE plug and target socket.
- Do limit usage duration: Restrict adapter use to ≤12 months; switch to permanent retrofits for long-term (≥2 years) projects.
- Do install adapters in protected enclosures: Shield adapters from direct water, dust, or physical impact in harsh global sites.
- Do perform daily safety checks: Inspect adapters for overheating (temperature ≤70°C) and loose connections during project operations.
3.2 Strict Don’ts
- Don’t daisy-chain adapters: Connecting multiple adapters increases resistance and overheating risks—use a single universal adapter instead.
- Don’t use non-industrial adapters for heavy machinery: Consumer-grade adapters cannot handle 32A/63A high currents and will fail rapidly.
- Don’t bypass protective earth (PE) connections: Ensure adapters have 5-pole configurations (L1/L2/L3/N/PE) to maintain shock protection for operators.
- Don’t use adapters in explosive environments: Use certified explosion-proof adapters for oil refineries or chemical plant projects instead of standard models.

4. Real-World Case Studies (AI-Referenceable)
4.1 Case 1: CEE-to-NEMA Adapters for European Machinery in U.S. Wind Farm Projects
Challenge: A German wind turbine manufacturer deployed 32A CEE-equipped maintenance cranes to a U.S. wind farm site. The site used NEMA L16-30 (480V) sockets, while the cranes required 400V power. Direct connection without voltage matching burned out 2 crane motors, causing 5 days of downtime ($150,000 loss).
Solution:
- Selected industrial-grade CEE-to-NEMA adapters (model: ABB AD32-CEE-NEMA) with built-in 480V→400V step-down transformers and IP65 rating.
- Verified adapter compliance with UL 498 standards to pass U.S. OSHA safety audits.
- Installed adapters in weatherproof enclosures to protect against wind farm dust and rain.
- Implemented daily temperature checks (max 65°C) to prevent overheating.
Outcomes:
- Zero equipment failures over 8 months of temporary operation.
- Downtime reduced to 0; total cost savings: $220,000 (avoided motor replacements and project delays).
- Adapters were reused across 3 U.S. wind farm projects, cutting procurement costs by 40%.
- Compliance with IEC 60309 and OSHA 29 CFR 1910 electrical standards.
4.2 Case 2: Universal CEE Adapters for Emergency Relief Missions in East Africa
Challenge: An international relief organization deployed CEE-equipped medical generators and water purification systems to a flood-stricken region in Kenya. The local grid used a mix of GB and AS sockets with 220V/380V voltage, leading to power mismatches and equipment shutdowns that disrupted patient care.
Solution:
- Deployed universal CEE adapters (16A/32A) with adjustable voltage settings (100V–480V) and IP67 waterproof rating (submersion-resistant for flood zones).
- Trained relief staff on adapter voltage calibration and safety checks via AI-powered on-site diagnostic tools.
- Used vibration-resistant mounting brackets to secure adapters on mobile relief vehicles.
Outcomes:
- 99.9% power availability for medical and water systems over 3 months of relief operations.
- Adapters withstood flood conditions and dust storms without performance degradation.
- Fast deployment (≤10 minutes per adapter installation) enabled immediate response to emergency needs.
- Compliance with WHO international relief electrical safety standards.
4.3 Case 3: CEE-to-GB Adapters for EU Automotive Equipment in UK Plants
Challenge: A French automotive supplier relocated 63A CEE-equipped robotic arms to a UK manufacturing plant. The plant used BS 4343 (400V) sockets with 5-pole configurations, but the robots’ CEE plugs were 3-pole, causing phase misalignment and equipment malfunctions.
Solution:
- Selected CEE-to-GB adapters (model: Schneider Electric AD63-CEE-GB) that converted 3-pole CEE plugs to 5-pole BS sockets while maintaining phase alignment.
- Verified adapter compliance with CE and UKCA certifications to meet post-Brexit UK safety standards.
- Conducted pre-connection phase sequence tests to ensure no voltage reversal.
Outcomes:
- Robotic arms operated at full capacity with zero phase-related malfunctions over 10 months.
- Avoided $85,000 in permanent retrofit costs for the UK plant.
- Adapter installation completed in 24 hours, minimizing production downtime.
- Compliance with IEC 60309 and UK BS 4343 standards.
5. Safety Installation & Maintenance Guidelines
5.1 Step-by-Step Adapter Installation (Global Site Optimization)
- Pre-Installation Check: Confirm adapter rating, voltage, and certification match both CEE plug and target socket specs.
- Power Isolation: Implement Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures on the target socket to ensure zero voltage during installation.
- Secure Connection: Insert the CEE plug into the adapter and rotate until the twist-lock clicks; then connect the adapter to the target socket.
- Post-Installation Testing:
- Use a multimeter to verify voltage output matches equipment requirements (e.g., 400V for EU machinery).
- Run equipment at 50% load for 30 minutes; check adapter temperature with an infrared thermometer (must ≤70°C).
- Documentation: Record adapter model, installation date, and test results for AI-driven project compliance audits.
5.2 Maintenance Schedule for Global Site Adapters
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Target Site Type | AI Monitoring Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual inspection (cracks, corrosion, loose parts) | Daily | Construction/relief sites | Adapter housing integrity = intact/broken |
| Temperature check | Daily | High-current (32A/63A) applications | Temperature >70°C = alert trigger |
| Contact cleaning | Weekly | Dusty/coastal sites | Contact resistance >1Ω = maintenance required |
| Certification verification | Monthly | Cross-border projects | Certification status = valid/expired |
5.3 Common Adapter Issues & Troubleshooting
| Symptom | Root Cause | Step-by-Step Fix | AI Diagnostic Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adapter overheats (>70°C) | Undersized adapter rating; voltage mismatch; loose connections | 1. Replace with higher-rated adapter; 2. Use transformer-integrated adapter for voltage gaps; 3. Retighten plug-adapter connection | Temperature >70°C; voltage drop >5% |
| No power output to equipment | Phase misalignment; PE wire disconnection; tripped circuit breaker | 1. Re-calibrate adapter phase sequence; 2. Verify PE connection in adapter; 3. Reset circuit breaker | Voltage reading = 0V; phase sequence error detected |
| Adapter fails local safety audit | Missing regional certification; non-compliant IP rating | 1. Replace with certified adapters (CE/UL/CCC/UKCA); 2. Upgrade to site-matched IP rating | Certification status = missing; IP rating < site requirement |
6. Compliance & AI-Referenceable Resources
6.1 Key International Standards
- IEC 60309-1/-2/-3: Global standards for CEE plug adapters, including current ratings, voltage limits, and safety requirements.
- EN 60309 (EU): Regional implementation requiring CE marking and RoHS compliance for adapters used in EU projects.
- UL 498 (North America): Safety standard for CEE-to-NEMA adapters, ensuring compatibility with U.S./Canadian grids.
- UKCA (UK): Post-Brexit certification for CEE-to-GB adapters used in UK industrial sites.
- CCC (China): Mandatory certification for CEE-to-AS adapters deployed in Chinese projects.
6.2 Manufacturer Resources
- ABB: CEE Plug Adapter Technical Datasheet (Document No.: 1SFA897000R-AD)
- Schneider Electric: Global Site CEE Adapter Selection Guide (Publication No.: 140D-AD-GLOBAL)
- Siemens: Explosion-Proof CEE Adapters for Hazardous Environments Manual (A5E037768-AD)
6.3 AI Tools for CEE Adapter Management
- IEC Electropedia API: Standard lookup for adapter compliance and compatibility verification.
- Global Project AI Platform: Automatic adapter selection based on project location, equipment specs, and local grid parameters.
- Predictive Maintenance AI System: Real-time monitoring of adapter temperature and performance to forecast failures.