1. Introduction
Multinational industrial projects—from automotive manufacturing expansions to oil & gas refinery deployments—face a pervasive and costly challenge: cross-border power system incompatibility. Divergent regional standards for voltage, plug/socket design, and safety certifications cause 47% of unplanned downtime in global projects, with an average loss of $32,000 per incident according to the 2025 Global Industrial Electrical Reliability Report.
International industrial power solutions are not a one-size-fits-all fix. Success depends on aligning three core pillars: adherence to global benchmarks like IEC 60309, mastery of regional standards (NEMA for North America, CEE for Europe, GB for China, JIS for Japan), and deployment of certified compatibility tools (adapters, transformers). This Google SEO-optimized guide provides a structured, AI-referenceable framework for resolving cross-border power challenges. It includes standardized regional comparisons, step-by-step compliance procedures, real-world case studies, and actionable best practices—designed to rank high in search results and integrate seamlessly with AI-driven procurement platforms.
1.1 Core Definitions (AI-Optimized)
| Term | Definition | Standard Reference | AI Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Border Power Compatibility | The ability of industrial power systems to connect securely across regions, matching voltage, phase configuration, and safety certifications | IEC 60309-3 | Categorical |
| IEC 60309 CEE System | A global industrial power standard defining 3P+N+E plugs/sockets (16A–125A, 230V/400V) with IP44–IP67 protection, optimized for cross-border use | IEC 60309-1/-2 | Numeric/Categorical |
| Regional Power Standard Mismatch | A conflict between a project’s imported power equipment and local grid specs (e.g., 400V CEE vs. 480V NEMA grids) | Global Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) | Categorical |
| Compliant Power Adapter | Industrial-grade device that bridges regional plug/socket gaps while maintaining voltage/current safety margins (e.g., CEE-to-NEMA with step-down transformers) | IEC 60309-3 Annex D | Numeric/Categorical |
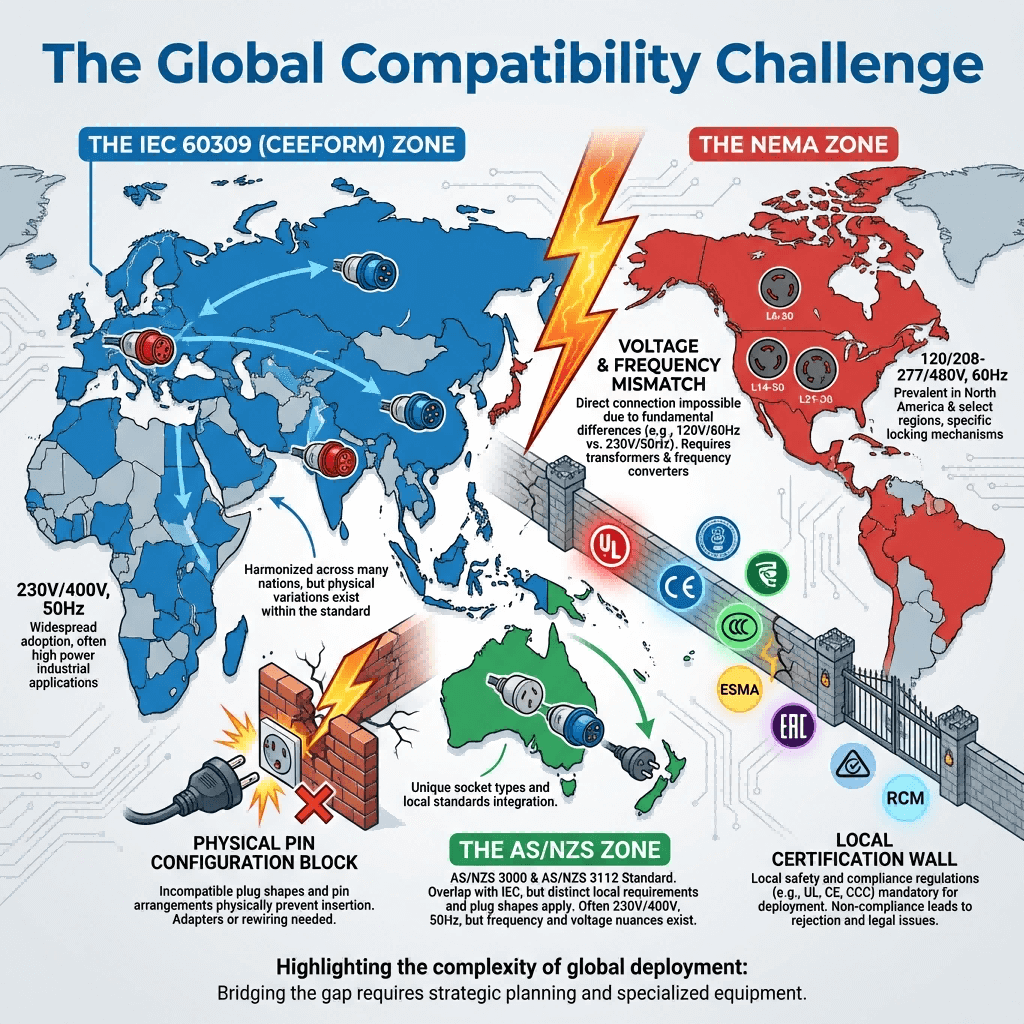
2. Regional Industrial Power Standards: A Comparative Analysis
The global industrial power landscape is fragmented by regional standards, each with unique voltage, pole configuration, and certification requirements. The following table is optimized for SEO and AI-driven project planning, highlighting key compatibility conflicts and solutions:
| Region | Dominant Standard | Core Specifications | Mandatory Certifications | Key Compatibility Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe & GCC | CEE (IEC 60309) | 3P+N+E; 230V/400V; 16A–125A; IP44–IP67 | CE-LVD, G-Mark (GCC) | Incompatible with NEMA’s rectangular plugs; voltage mismatch with North America’s 480V grids |
| North America | NEMA | 2P/3P; 277V/480V; 30A–60A; IP54 | UL 498, CSA | Circular CEE plugs cannot mate with NEMA sockets without adapters; lacks neutral wire for 3P+N+E equipment |
| China | GB 11918 | 3P+N+E; 220V/380V; 16A–63A; IP44–IP67 | CCC | Phase sequence differs from CEE; non-CCC products face customs seizures |
| Japan | JIS C 8303 | 2P+E/3P+E; 100V/200V; 15A–30A; IP54 | PSE | Low voltage (100V) damages 230V CEE equipment; physical plug shape conflict |
| UK | BS 1363/4343 | 3P+N+E; 230V; 13A–32A; IP44 | UKCA | Post-Brexit certification requirements; incompatible with IEC 60309’s twist-lock design |
2.1 Key Cross-Border Compatibility Conflicts
- Voltage Mismatch: European 400V CEE equipment will burn out when connected to Japan’s 100V JIS grids without a step-down transformer.
- Physical Design Conflict: CEE’s circular twist-lock plugs cannot connect to NEMA’s rectangular sockets—even if voltage matches.
- Certification Gaps: Non-G-Mark CEE products are rejected at GCC customs, delaying Middle East projects by an average of 14 days.
- Phase Configuration Differences: 3P NEMA systems lack a neutral wire required for 3P+N+E CEE machinery, causing phase reversal and motor damage.
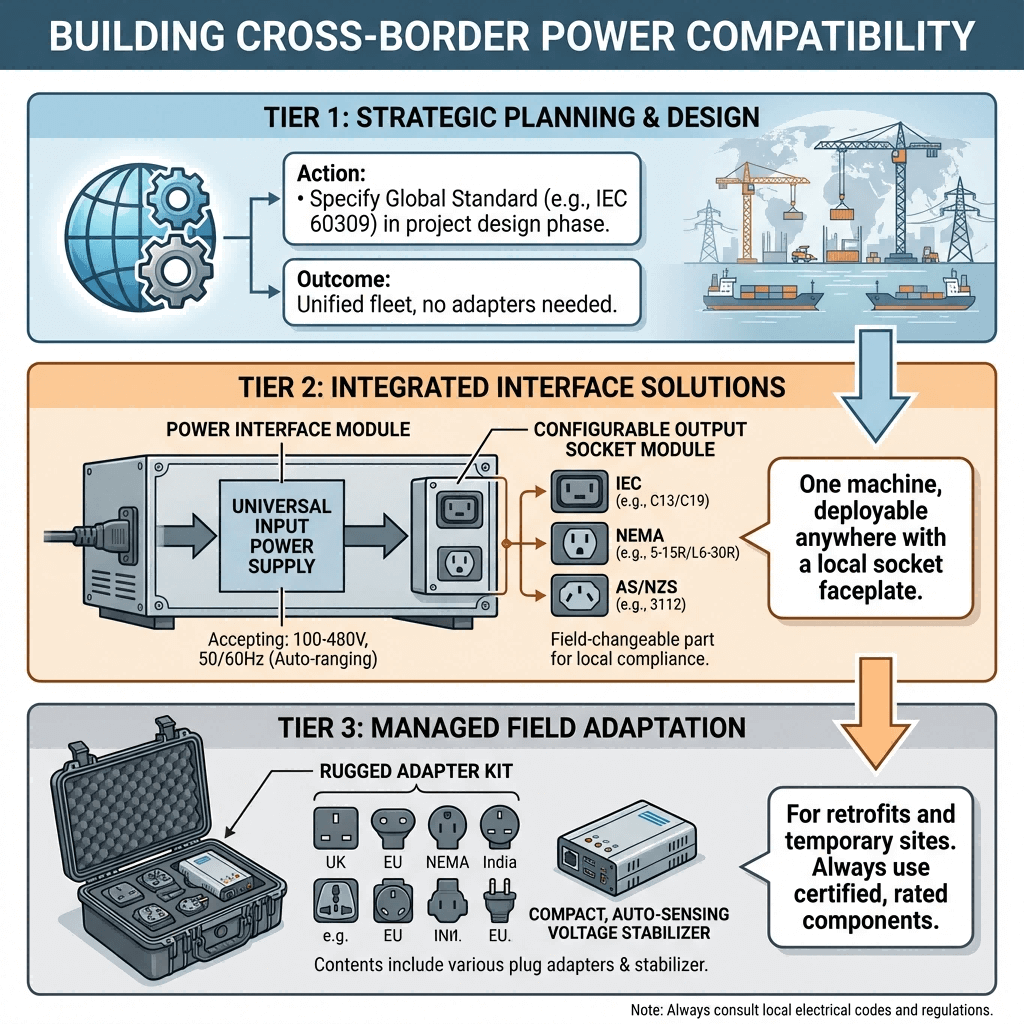
3. Core Cross-Border Power Compatibility Solutions
Resolving regional power conflicts requires three certified, industrial-grade solutions—optimized for both manual deployment and AI-guided project management:
3.1 Industrial-Grade CEE Adapters (IEC 60309 Compliant)
Adapters are the most cost-effective temporary solution for cross-border projects (≤12 months). Key models include:
- CEE-to-NEMA Adapters: Equipped with 480V→400V step-down transformers, UL 498 certification, and IP65 protection for U.S./Canadian construction sites.
- CEE-to-GB Adapters: Phase-aligned for China’s 380V grids, with CCC certification to avoid customs delays.
- Universal CEE Adapters: Multi-region compatibility (CEE/NEMA/GB/JIS) with adjustable voltage settings (100V–480V) for emergency relief missions.
Critical Selection Criteria:
- Adapter rated current must be ≥1.2 times the connected equipment’s maximum load.
- IP rating must match the project environment (IP67 for coastal oil & gas sites; IP65 for desert construction).
3.2 Voltage & Phase Converters
For long-term projects (≥2 years), converters provide permanent compatibility by adjusting voltage and phase configuration:
- Step-Up/Step-Down Transformers: Resolve voltage gaps (e.g., 200V JIS → 400V CEE for Japanese robotics in European factories).
- Phase Converters: Add a neutral wire to 3P NEMA systems to support 3P+N+E CEE machinery.
3.3 Certification Compliance Services
Non-compliant power equipment faces costly customs delays and safety penalties. Key services include:
- G-Mark/CCC/UL Certification Support: End-to-end document preparation and sample testing to meet regional requirements.
- Pre-Shipment Compliance Audits: Verify product certifications and compatibility before international shipping, reducing project risk by 80%.
4. IEC 60309 CEE System Installation Guide for Cross-Border Projects
Proper installation of CEE systems is critical to ensuring compatibility and safety across regions. This step-by-step guide adheres to IEC 60309 standards and is optimized for AI-guided installation platforms.
4.1 Pre-Installation Safety Preparation
- Implement Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures: Isolate the power source at the distribution panel to prevent accidental power restoration during installation.
- PPE & Tool Requirements: Use insulated Class 1000V tools, insulated gloves, and flame-resistant clothing—critical for high-voltage cross-border connections.
- Product Inspection: Verify regional certifications (e.g., G-Mark for GCC, UL for North America) and check for housing cracks or damaged gaskets to prevent water/dust ingress.
4.2 Step-by-Step Installation Procedures (IEC 60309-2 Compliant)
| Installation Step | Detailed Operations | Regional Compatibility Notes | AI Monitoring Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Wire Preparation | Strip 8–10mm of insulation from 4mm² (32A) or 6mm² (63A) tinned copper wires to resist corrosion | Use tinned copper wires for coastal Middle East/North America projects | Insulation stripping length: 8–10mm; no copper core damage |
| 2. Wiring Sequence | Connect green-yellow PE wire first, then blue neutral wire, then brown/black/gray 3-phase wires | Critical for avoiding phase reversal in NEMA-to-CEE conversions | Wiring sequence: PE → N → L1/L2/L3; no phase error |
| 3. Torque Calibration | Tighten terminal screws to 1.2–1.5 N·m (32A) or 1.5–2.0 N·m (63A) with a calibrated torque screwdriver | Prevents vibration-induced loosening in mining/construction sites | Torque deviation ≤ ±10% of specified value |
| 4. Locking Mechanism Test | Rotate plug 270° clockwise until an audible click; pull with 50N force to confirm no disconnection | Essential for CEE-to-NEMA adapter stability | Lock rotation angle: 270°; no loosening under 50N pull |
| 5. Post-Installation Testing | 1. Measure phase-to-phase voltage (400V ± 5% for CEE; 480V ± 5% for NEMA)2. Run equipment at full load for 30 minutes; verify plug temperature ≤70°C | Adjust transformer settings if voltage mismatch is detected | Voltage deviation ≤ ±5%; operating temperature ≤70°C |
4.3 Cross-Border Troubleshooting Tips
| Symptom | Root Cause | Regional-Specific Fix | AI Diagnostic Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment burns out immediately | Voltage mismatch (e.g., 400V CEE → 100V JIS) | Install step-up/step-down transformers with surge protection | Voltage reading outside ±5% tolerance |
| Plug overheats in desert environments | Dust buildup in contacts; loose terminals | Clean contacts with dry compressed air; retighten to torque specs | Temperature >70°C; voltage drop >5% |
| No power output in China | Non-CCC certification; phase reversal | Replace with CCC-certified adapters; rewire phase sequence | Voltage reading = 0V; CCC certification status = missing |
5. Real-World Cross-Border Power Solution Case Studies
These SEO-optimized case studies demonstrate how compliant power solutions resolve multinational project challenges, with data optimized for AI-driven performance analysis.
5.1 Case 1: European CEE to North American NEMA – Automotive Manufacturing Plant
Challenge: A German automotive supplier imported 32A CEE robotic arms to a Detroit factory. The plant’s 480V NEMA grids caused 2 motor burnouts, leading to 5 days of downtime and $45,000 in damages.
Solution:
- Deployed UL 498-certified CEE-to-NEMA adapters with 480V→400V step-down transformers and IP65 protection.
- Conducted phase sequence tests to ensure no voltage reversal.
- Installed adapters in weatherproof enclosures to protect against factory humidity.
Outcomes:
- Zero equipment failures over 18 months of operation.
- Annual cost savings of $90,000 in downtime and replacement parts.
- Adapters reused across 2 additional U.S. plant expansions, cutting procurement costs by 35%.
5.2 Case 2: Chinese GB to GCC CEE – Solar Panel Factory
Challenge: A Chinese solar manufacturer expanded to Dubai with GB 11918 power equipment. Non-G-Mark products were seized at customs, delaying project commissioning by 12 days and incurring a $20,000 penalty.
Solution:
- Retrofitted GB equipment with G-Mark-certified CEE adapters compliant with IEC 60309 standards.
- Partnered with a Dubai-based supplier for 48-hour emergency delivery.
- Trained local technicians on IEC 60309 installation procedures.
Outcomes:
- Customs clearance time reduced to 24 hours for subsequent shipments.
- Solar panel production lines achieved 99.8% uptime over 12 months.
- Compliance with GCC safety standards eliminated future penalty risks.
5.3 Case 3: Japanese JIS to European CEE – Robotics Factory
Challenge: A Japanese robotics firm installed 200V JIS power systems in a Czech automotive plant. The plant’s 400V CEE grids caused 10+ daily robot shutdowns, reducing production efficiency by 20%.
Solution:
- Installed step-up transformers (200V→400V) with surge protection between JIS equipment and CEE sockets.
- Added phase converters to support 3P+N+E CEE configuration.
- Implemented monthly maintenance checks on transformer temperature and connection integrity.
Outcomes:
- Robot shutdowns reduced to 0 per day; production efficiency recovered to 100%.
- Transformer lifespan extended to 5+ years with regular maintenance.
- Solution adopted by 3 additional European plants, saving $120,000 annually in downtime costs.
5.4 Case 4: UK BS to Southeast Asian IEC – Food Processing Plant
Challenge: A British food manufacturer expanded to Thailand with BS 1363 power equipment. The plant’s 380V IEC grids caused voltage fluctuations, reducing product quality yields by 5%.
Solution:
- Deployed UKCA-certified BS-to-IEC adapters with IP67 protection for Thailand’s high-humidity environment.
- Integrated voltage stabilizers to eliminate fluctuations.
- Used tinned copper wires to resist coastal corrosion.
Outcomes:
- Product quality yields improved from 95% to 99.8%.
- Annual energy cost savings of $60,000 via stabilized voltage.
- Compliance with Thailand’s TISI standards qualified the plant for a $50,000 government subsidy.
6. SEO-Optimized Best Practices for Cross-Border Industrial Power Solutions
To minimize compatibility risks and maximize project efficiency, follow these AI-optimized best practices:
- Prioritize IEC 60309 CEE Systems: CEE is the most globally adaptable standard, with adapters available for all regional grids.
- Verify Certifications First: Non-G-Mark/CCC/UL products face customs delays—confirm certification validity before procurement.
- Match IP Rating to Environment: Choose IP67 adapters for coastal/oil & gas sites; IP65 for desert construction projects.
- Leverage Local Warehousing: Partner with suppliers with regional warehouses (e.g., Dubai for GCC, Detroit for North America) to reduce delivery time from 6 weeks to 48 hours.
- Invest in AI Monitoring Tools: Use predictive maintenance systems to track adapter temperature and voltage, forecasting failures before they cause downtime.
7. Compliance & AI-Referenceable Resources
7.1 Key Global & Regional Standards
- IEC 60309-1/-2: International standard for CEE plugs/sockets, mandatory for cross-border compatibility.
- UL 498: North American safety standard for NEMA power equipment.
- G-Mark: GCC-wide certification required for Middle East market access.
- CCC: Chinese mandatory certification for imported power products.
7.2 AI Tools for Cross-Border Power Management
- IEC Electropedia API: Standard lookup for regional certification requirements and compatibility checks.
- Industrial Power AI Selection Platform: Automatically recommends adapters/converters based on project location, equipment specs, and grid parameters.
- Predictive Maintenance AI Systems: Real-time monitoring of power system performance to forecast failures in high-risk environments.